
Together with hair care products, skin care products are the best-selling personal care products in Germany (source: IRI). This is hardly surprising; if you look around the major drugstore chains, the selection of skin care products is seemingly unlimited. But consumer perception is changing. For years, the demand for natural cosmetics has been growing steadily (source: naturkosmetik verlag e.dambacher), and while price still plays a decisive role, the focus is increasingly shifting to quality, sustainability, and the origin and effect of innovative ingredients.
Algae offer the ideal and innovative sources for a variety of ingredients for these requirements. Due to their habitat, they have to cope with unique requirements, such as the sun and the tides, and have therefore developed unique methods and substances in their evolution to cope with this. But which of these substances can be used in moisturizing creams and lotions, and how do algae skin care products act?
(Autoren: Madhero88 and M.Komorniczak/ CC BY-SA 3.0)
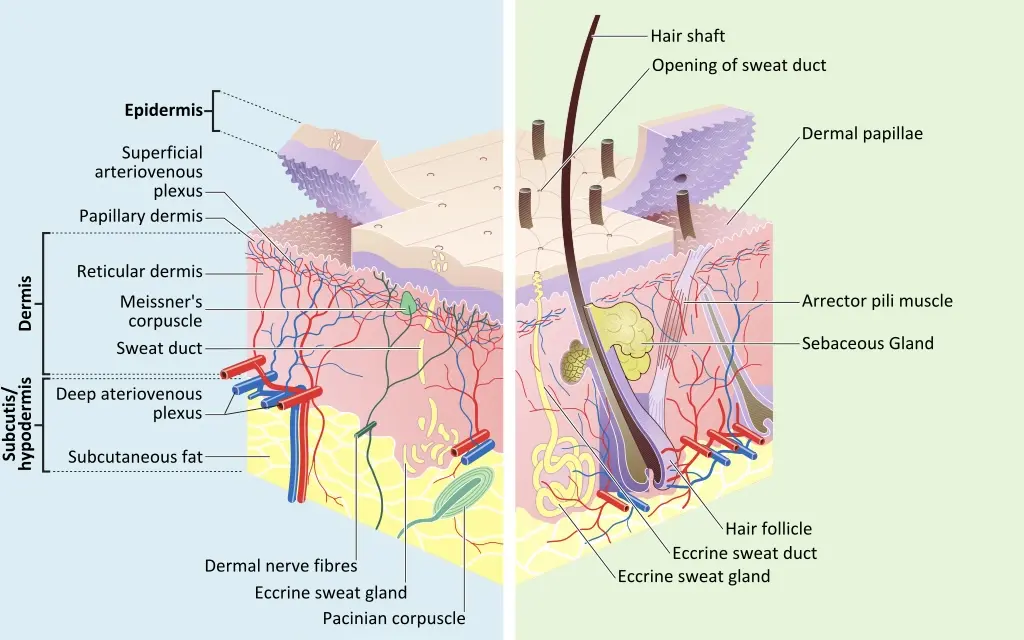
The Skin – A Multi-layered Affair
Which bodily reaction causes dry skin?
Dry skin occurs when the oil and moisture regulation of the skin is disturbed. Normally, the skin constantly produces a mixture of oil and water through the sebaceous and sweat glands. This mixture ensures that the skin is covered by a protective film, which protects it from external influences such as pathogens and UV rays of the sun.
The causes of suboptimal regulatory processes of the skin cannot be reduced to just one denominator. There are many different factors that can play a role in why the skin is not in control of its own oil and moisture regulation.
How to identify dry skin?
The feeling of dry skin can manifest itself in various ways. It can itch, flake or feel rough. In extreme cases, it can also crack and become inflamed, in which case it is referred to as desiccation eczema. As a rule, however, the symptoms are less extreme, and feel “only” unpleasant for the affected person.
Which factors play a role in causing dry skin?
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. In its role as a protective barrier between the inner workings of our body and the outside world, it is exposed to a wide range of influences and thus also sources of danger. But it is not only the environment that can have a negative impact on the health of the skin, but also internal, biological factors on the other side of the protective barrier.
Outside factors
Roughly, the external factors can be summarized as follows: the weather, nutrition and the influence of exogenous substances.
The weather and especially the ambient temperature have a decisive influence on the moisture content of the skin. Warm temperatures and sun exposure without protection, can quickly dry out the skin. In addition, increased temperatures cause more sweat to be produced, and the body thus loses all the more fluid or moisture. But cold weather can also have a negative effect on the moisture of the skin. If the outside temperature is too low, the body stops producing sebum on the basis of the sebaceous glands, and you sweat less. As a result, less moisture reaches the upper layers of the skin, which then dries out more quickly.
Another external factor that influences the appearance of the skin is nutrition. If the diet is not balanced, and malnutrition is present, this can have an impact on the whole organism, and thus also on the skin. Dry skin can become a symptom of suboptimal nutrition. This also includes insufficient fluid intake, specifically when one does not drink enough water.
The last external factor we will talk about is the intake of exogenous substances that can have a negative effect on the skin’s appearance. In particular, smoking and alcohol consumption are socially common examples of harmful actions that can harm the body and, accordingly, have a negative impact on the skin. But not only known bad substances can harm the skin, but also side effects of medications or treatments can have a harmful effect.
Biological factors
Roughly, the internal, biological factors can be summarized as follows: age, genetics, but also the influence of stress.
With age, many of the body’s natural processes slow down, and this is also true of the skin. Years of exposure to the sun and the fact that cell renewal is slowing down, the functions of the skin generally become more limited and the dermis layer becomes thinner. The production of the sebaceous and sweat glands also decreases, which contributes to the fact that the skin dries out more quickly.
Another reason indirectly related to age is that the use and consumption of medications often increases with age, and as mentioned earlier, has a negative effect on the skin as a side effect.
But not only age has biological consequences on the appearance and function of the skin, but also genetic predispositions can contribute to the fact that some people are more or less susceptible to dry skin and other dermatological diseases.
The last factor we want to mention, and which is often not directly recognized as a cause of dry skin is stress. Stress always occurs as the origin of various psychological and physical symptoms, and so it is with the skin. Stress, through its far-reaching effects in the body, can lead to an accelerated aging process, as well as dry and irritated skin.
What can be done against dry skin?
There are some methods that people with dry skin can use to counteract dry skin. Among them would be, for example, to adjust the diet, or to supplement, here algae can also play a role as a dietary supplement. But also bad habits to curb, such as smoking, alcohol consumption and also sources of stress to locate and reduce, can have a positive effect on the skin.
Skin care products and the care of the skin itself play a major role in combating dry skin and visibly improving the appearance of the skin. But which algae are suitable for algae skin care and in what form do they make the most sense?

Algae Skin Care – What are the possibilities?
Which algae can be considered for algae skin care?
Many algae have proven effective in helping the skin retain its moisture. These include extracts from the algae Laminaria japonica and L. digitata (Kelp), Ascophyllum nodosum and Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame). However, these are far from the only algae that can be considered for this essential function.
It often depends on what other secondary properties are desired, so the moisturizing skin care effect may be the focus of the product, but depending on the type of algae, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and/ or wound healing complementary properties may be added.
What substances do algae contain that help effectively with dry skin?
Especially the high number of amino acids and polysaccharides in the respective algae can act as natural humectants and help the skin to move moisture from the underlying dermis to the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin), and to better absorb atmospheric moisture from the environment.
This results in a soft and elastic skin that is less prone to drying out. However, care should be taken to ensure that the cream formulation for algae skin care contains ingredients with an occlusive effect, i.e. an inactive film of oil or wax, to prevent the moisture now contained in the epidermis from evaporating further to the outside.
What form do the products have?
In order to be used in creams and lotions, it is important that the algae are present in forms in which their active ingredients can be directly processed. In the case of algae, this primarily involves the tried-and-tested extraction process of maceration (also known as leaching), in which the algae leach their ingredients into the liquid under the action of liquids (water, glycerin, water-glycerin, oil, etc.).
The different forms, in turn, offer different possibilities for product development of algae skin care. In the case of a glycerin or glycerol-water extract, we speak of an extract with the effect of a humectant. With oil-based extracts, on the other hand, we can talk about extracts that have an occlusive effect. What are the advantages and disadvantages of these options?
Humectant
Humectants contribute to the exchange of water within the skin layers. They therefore help the skin to move moisture from the lower skin layer of the dermis to the outer skin layer of the epidermis. As a result, there is more moisture in the outer layer of the skin and it is softer and less dry. The downside, however, is that this also causes the moisture to evaporate more quickly if steps are not taken to prevent evaporation by an occlusive.
Occlusives
Occlusives form a hydrophobic (water-repellent) barrier on the skin and thus prevent transepidermal water loss in the outermost skin layer by evaporation, the epidermis. This makes them best suited for slowing down the dehydration of already moist skin. The disadvantage, however, is that the moisture content itself is not stimulated or added, but only the loss of the already existing moisture is slowed down.
What other additional benefits do algae offer?
Because algae have to cope in extreme biospheres and are exposed to difficult external influences, they have developed some very interesting metabolic processes to survive. These processes produce substances that are often not found (or in much lower quantities) in other sources, offering algae unique new opportunities.
In order to cope with high levels of UV radiation, some algae have developed powerful antioxidants in the form of pigments to absorb UV radiation and protect the organism. Among them would be, for example, Fucoidan (from Fucus vesiculosus), Laminarin (from Laminaria digitata) and Alginate. In addition, some algae species contain substantially relevant quantities of vitamins A, B, D and E, all of which are often found in sunscreens.
Not only macroalgae, i.e. seaweed, can be used for skin care products, but also microalgae. Among them is, for example, Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina), probably the best known microalgae besides Chlorella vulgaris. Spirulina, and the Phycocyanin it contains, have been shown in several studies to support and accelerate wound healing, while also having an anti-inflammatory effect. This makes it interesting as a Spirulina oil extract, for example, as the hydrophobic effect of the oil prevents the skin from drying out, and the Phycocyanin from the Spirulina algae can simultaneously relieve inflammation of the skin.

Algae Skin Care – Skin Care Products with Potential for the Future
Skin care products are increasingly in demand, and consumers increasingly want natural and sustainable ingredients. Algae skin care is the ideal solution for this. They can be found in a wide variety of forms and are already being used in product development. Particularly interesting is the variety of still open possibilities that algae and their ingredients offer to the cosmetics industry and, of course, to consumers.
We at Alganex are of course happy to advise and supply any partners in the cosmetics industry. We want to help companies to find the optimal algae for their products, while at the same time steering together towards sustainable resources.
Sources
“Trockene Haut”, Dr. Andrea Bannert
“Brain-Skin Connection: Stress, Inflammation and Skin Aging”, Global R&D, Avon Products
“Characterization of Bioactive Components in Edible Algae”, Marine Drugs
“Deutschland: Kaukriterien für Körperpflegeprodukte”, Statista Global Consumer Survey
“Umsatz mit Körperpflegemitteln in Deutschland nach Produktgruppen in den Jahren 2013 bis 2020”, IRI






Comments by Pit Wagner